Cost-effectiveness of homeopathy
Health economic research aims to establish a scientific basis for efficient distribution of limited healthcare and financial resources, whilst also ensuring a consistent delivery of high-quality care to patients. The health economic methods used to assess cost-effectiveness of conventional medical treatments can also be applied to homeopathy.
A systematic review considered the highest level of scientific evidence – was published in January 2024, providing an overview of cost-effectiveness studies of homeopathy1. In all 21 studies included in this review, homeopathy showed similar or better clinical effectiveness compared to the control groups, with a clear positive trend for cost-effectiveness:
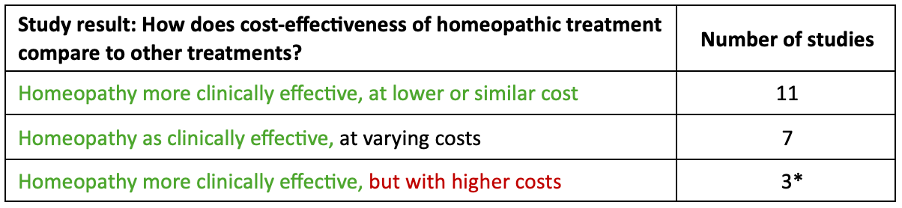 *2 of these studies were shown to be cost-effective through incremental cost effectiveness analysis.
*2 of these studies were shown to be cost-effective through incremental cost effectiveness analysis.
It is worth noting that the two most recently published studies included in the review3,4 are among those with the highest quality rating. In addition to a well-chosen study design, both used state-of-the-art economic evaluations. The authors of the updated review stress the importance of maintaining this level of excellence in future economic evaluations of homeopathy.
- for children under 12, additional SilAtro-5-90 treatment is always cost-effective (regardless of the severity of recurrent tonsillitis), reducing the number of acute throat infections at a lower cost than using conventional treatment alone
- for adults and children aged 12 years and older with ‘severe’ recurrent tonsillitis (more than three acute throat infections per year), SilAtro-5-90 helped avoid expensive surgical tonsillectomy.
Further high quality research on the cost-effectiveness of homeopathy is clearly warranted: building on these encouraging findings will determine more definitively whether homeopathy can play a role in managing healthcare costs in future, whilst maintaining levels of clinical effectiveness comparable to existing treatments.
Further information
Cost-effectiveness review (Ostermann et al. 2024 synopsis.
Study evaluating cost-effectiveness of homeopathic treatment for recurrent tonsillitis (Ostermann et al. 2021 synopsis)
Insights into funding of Homeopathy in the UK
- Ostermann T, Burkart J, De Jaegere S, et al. Overview and quality assessment of health economic evaluations for homeopathic therapy: an updated systematic review. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res, 2024;24:117-142 [PubMed] [FullText]
- Viksveen P, Dymitr Z, Simoens S. Economic evaluations of homeopathy: a review. Eur J Health Econ, 2014;15:157-74 [PubMed]
- Kass B, Icke K, Witt CM, Reinhold T. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treatment with additional enrolment to a homeopathic integrated care contract in Germany. BMC Health Serv Res, 2020;20:872 [PubMed] [FullText]
- Ostermann T, Park A-L, De Jaegere S, Fetz K, Klement P, Raak C, McDaid D. Cost-effectiveness analysis for SilAtro-5-90 adjuvant treatment in the management of recurrent tonsilitis, compared with usual care only. Cost Eff Resour Alloc, 2021;19:60 [FullText]
- Palm J, Kishchuk VV, Ulied A, Perotti Fernández J, De Jaegere S et al. Effectiveness of an add-on treatment with the homeopathic medication SilAtro-5-90 in recurrent tonsillitis: An international, pragmatic, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Complement Ther Clin Pract, 2017; 28:181-191 [PubMed]




